WHAT IS FLEXIBILITY AND ITS TYPES
What is flexibility and its types-Flexibility means the ability of an individual to bend easily without breaking or the ability to move his or her joints through a full range of motions. It is one of the motor components of physical fitness. Flexibility in the body allows for a maximum range of movement without much internal resistance. Flexibility helps to stretch without straining themselves. Flexibility is the ability that helps insufficient expansion to perform the MOTION. Flexibility is neither ability for compatibility, nor is it equivocation ability. Flexibility varies from person to person, it depends on the ligaments, tendon, types of joints, and muscles. Flexibility depends on the contraction and expansion of muscles. It can be defined as the range of motion in a joint or group of joints or the ability to move joints effectively. Flexibility in the movement of the sports is a primary requirement based on sufficient quantity and sufficient qualities.
IMPORTANCE OF FLEXIBILITY
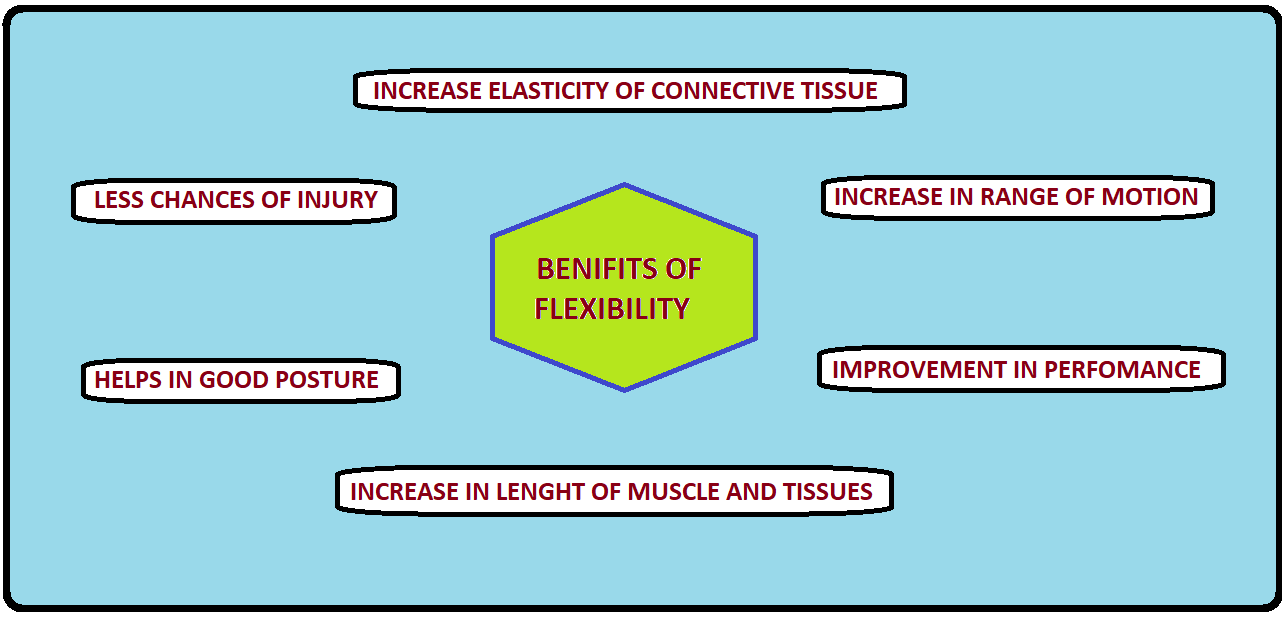
- Flexibility protects against INJURIES in the game.
- Flexibility is important for performing actions at the highest level.
- Flexibility affects skills.
- Has a greater effect on endurance actions.
- It helps in developing the force.
- Develops singular abilities.

FACTOR DETERMINING FLEXIBILITY
What is flexibility and its types-There are various factors that affect flexibility in different ways like internal factor and external factor
INTERNAL FACTOR OF FLEXIBILITY
The anatomical structure of the JOINTS
Different joints make their own different movements and determine the movements of the joints. The shoulder joints of the players are more powerful than those of the hips. Knee and elbow joints stir evenly due to their physical structure and limited area. Joints and structure determine mostly on inheritance. Body structure in adolescence cannot be changed by training.
Length and elasticity of the muscles and ligaments
The length of the ligaments depends on the movements of the joints. Ligaments fibers are not usually dilated. As the length of the ligament fibers increases, the range of movements also increases.
Strength of the muscles
Muscle strength should be enough to prevent resistance to external strength. Most of the activities of the game are done to prevent external force.
Co-ordination
When the body is in motion, the extension of the movements of the body is considered an important basis of coordination. Skills are also a basis due to which affect the movements and flexibility of the body.
Temperature of muscles
The temperature of the muscles also affects the flexibility because when the temperature of the muscles is sufficient then it will be able to perform any kind of movements, which reduces the chance of any type of muscular tension or cramp.
EXTERNAL FACTORS OF FLEXIBILITY
Atmospheric temperature
Flexibility is also affected by the temperature of the atmosphere. For example, if you are stretching in the morning, afternoon, or evening, then in the evening, the muscle becomes more stretched because the body temperature also increases with the external temperature.
The age factor in flexibility
Flexibility also decreases with aging, as stiffness in muscles begins to increase. It is generally seen that by 12 years of age, flexibility develops very well and after 12 years there is not much improvement and after 18 years it starts becoming less. Flexibility can be increased to some extent by proper training.
Proper Warm-up
Stretching well after the warm-up makes the body more flexible because the heart rate in the warm-up also increases the blood flow in the muscles. The range of motion increases by up to 20% after a proper warm-up.
Sex factor in flexibility
Girls have more flexibility than boys because their anatomical structure helps in this. And their percentage is also high in fat percentage, which is an important factor of flexibility.
Body type
It depends on the physical structure. In which people with endomorph structure have more flexibility.
Fatigue
Muscles become stiff when the body is tired, which reduces the flexibility of muscles. Active fatigue decreases with fatigue, but passive flexibility increases.
TYPES OF FLEXIBILITY
What is flexibility and its types- Mainly there are two types of flexibility
Active flexibility
Static flexibility
Dynamic flexibility
Passive flexibility
PASSIVE FLEXIBILITY- The ability of a joint to perform the movement with a full range of motion with the help of a partner or external help or in other words we can say this is the maximum flexibility that a player can achieve with the help of an assistant or partner.
ACTIVE FLEXIBILITY- It is the ability to perform the movement without any external help; this is the maximum flexibility that a player receives from their muscle contraction without any help.
- STATIC FLEXIBILITY- To perform the movement with a full range of motion in a static or stable position like forwarding bending, side stretch, and yoga asanas, etc. static flexibility requires no voluntary muscular activity.
- DYNAMIC FLEXIBILITY- To perform the movement with a full range of motion in moving or operational like gymnastics etc. Dynamic flexibility is also called kinetic flexibility. Dynamic flexibility requires voluntary muscular action.
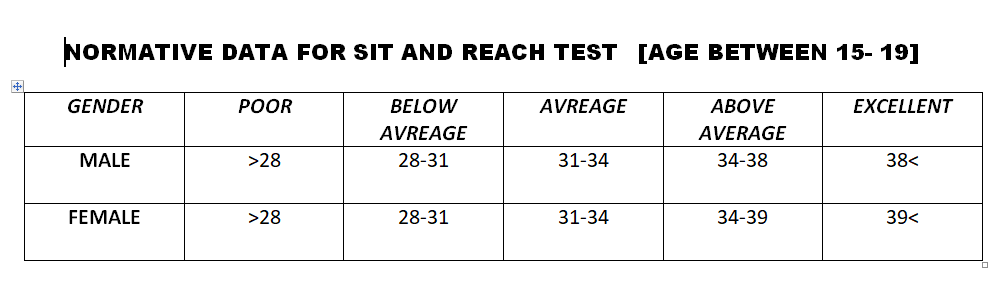
INSTRUMENT TO MEASURE FLEXIBILITY– FLEXO METERE or it can be measure by Sit and reach test, chair sit and reach test for lower back flexibility [for senior citizen]

METHODS TO IMPROVE FLEXIBILITY
WHAT IS STRETCHING – Stretching is a form of physical activity that can lead to an increase in flexibility. Stretching is a form of physical exercise in which a specific skeletal muscle is deliberately elongated, in order to improve the muscle felt elasticity and reaffirm comfortable muscle tone.
- Ballistic stretching
- Slow stretching method
- Active stretching
- Static stretching
- Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation [PNF]
- Passive stretching
BALLISTIC STRETCHING–
This method is the oldest method of stretching exercise. In this method, the joint stretches to the maximum range in rhythm or to perform stretching exercises while in motion. In this, the stretching movement is done with a swing action. The ballistics method is also called the dynamic method because this method used the momentum generated from repeated movements to stretch the muscle. This is a very effective method but it may cause overstretching of muscles which results in muscle soreness and injury, for Example- swinging of back forward and backward, etc.
SLOW STRETCHING METHOD-
In this method, the joints are gradually stretched to the maximum range and hold in the same position for some time, then return to the same position. For best effect, hold in the maximum stretch for 3 to 8 seconds, holding for longer than that does not increase the effect. This method is very effective in improving passive flexibility. Seek partner’s help to make it more effective.
ACTIVE STRETCHING-
In the active stretching method we have to hold a particular position and maintain it exclusively with your muscle’s strength.
STATIC STRETCHING-
All the yogic asanas come under this stretching. It involves slowly and gently moving into a stretch position and holding for a certain period of time. In this muscle stretch through a full range of motion until the tension is felt in the group of muscles and hold for 15-30 sec and relax vice versa.
PASSIVE STRETCHING-
In passive stretching movement is done with an outside force such as a partner, or any type of equipment that allies stretch to a relaxed joint.
PROPRIOCEPTIVE NEUROMUSCULAR FACILITATION [PNF]-
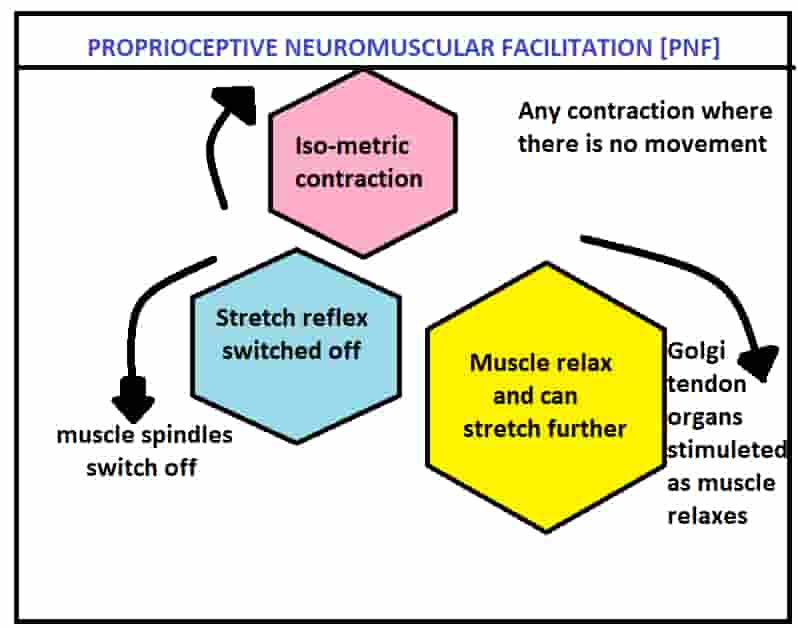

PNF may be superior to another stretching method because they facilitate muscular inhibition. Usually performed with a partner and involve both passive movement and active [concentric and isometric] muscle action. This muscle is first contracted [antagonistic muscles] isometrically for 6-7 seconds after this the muscle is gradually stretched to its maximum limit and is held in this position for 8-10 seconds. This procedure is too repeated 4-8 times for each muscle group.
READ MORE ABOUT – WHAT IS STRENGTH AND ITS TYPES





