WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF JOINTS IN THE BODY
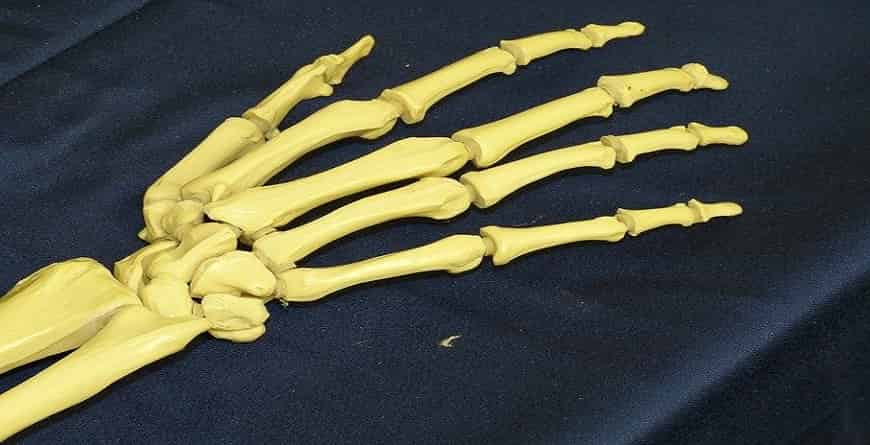
Types of joints in the body- The skeletal structure of the body is made up of many types of bones, small, long, thin, flat, round, etc. and the muscles provide symmetry to them, but the dynamic joints gain the ability to move the body. Where two bones meet in the body, the joint is formed; the joint is fixed or moving. Static joints are those that lie between the bones facing each other and are able to separate the layer of thin connective tissue. The joints are classified on the basis of structurally and functionally.
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINT BASED ON FUNCTIONALITY: –
Even on the basis of functionality, there are different types of joints in the body joints are classified into three classes. At the place where bones are formed, they can do a lot of movement, but there are some joints in which there is no ability to move at all. Some joints may have only light movements. Some joints have the ability to move freely.
- SYNARTHROSES {Immovable joints}
- AMPHIARTHROSES {Slightly movable joints}
- DIARTHROSES {Movable joints}
Generally speaking, fibrous joints are usually movable joints and synovial joints are generally movable joints, synarthroses. But not all joints can be divided under this classification. Because there are some joints that are also slightly moving like the lower joint of the fibula and tibia.
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINT BASED ON COMPOSITION:-
The joints are divided into three categories such as: –
- FIBROUS JOINTS
- CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS
- SYNOVIAL JOINTS
FIBROUS JOINTS
Fibrous joints lack the joint cavity, and (fibrous connective tissues) bind the bones together. [types of joints in the body] Because they are interlinked, fibrous joints are usually fixed in adults.
It is of three types:-
- SUTURES
- SYNDESMOSES
- GOMPHOSES
SUTURES: –
The joint lines found in the middle of the cranial bones are fibrous or immovable joints. In adults, these bones do not move after joining and become completely stable. The teeth at the edges of the joining bones are like saws, which fit into the teeth of another bone and make sutures joint. At the time of the birth of the baby, there is a clear line of fibrous tissue between the bones, which allows the edges of the bones to slide slightly on top of each other. This makes it easier for the head of the baby to be molded while coming out of the birth canal, due to the flexibility of the cranial sutures in the fetus and children, brain growth is possible, in adults, the fibers of the connective tissue between the bones are converted into bone. And bone is permanently joined; this kind of joint is called bone combination. The teeth at the edges of the joining bones are like saws, which fit into the teeth of another bone and make sutures joint. At the time of the birth of the baby, there is a clear line of fibrous tissue between the bones, which allows the edges of the bones to slide slightly on top of each other. This makes it easier for the head of the baby to be molded while coming out of the birth canal, due to the flexibility of the cranial sutures in the fetus and children, brain growth is possible, in adults, the fibers of the connective tissue between the bones are converted into bone. And the bones are permanently attached. This type of treaty is called bone combination.
SYNDESMOSES: –
It is an immovable joint in which the bones are close but do not touch each other and are connected by interosseous ligaments. The speed of such a joint depends on the distance between the bones and the flexibility of the fibrous connective tissue. Such an immovable joint is formed in the inferior tibiofibular joint, where there is limited movement, which gives strength to this joint. While excessive movement occurs by the interosseous ligament located between the radius and ulna, which also has pronation and supination movements of the forearm.
GOMPHOSIS: –
It a type of fibrous joint, which is the sign of a nail or peg and socket. This type of treaty is made by fitting it into the tooth socket of the tooth root.
CARTILAGINOUS JOINTS IN THE BODY
In cartilaginous joints, the bones are attached to the plate of hyaline cartilage or the pad of fibrocartilage. In such treaties, there is a lack of joint cavity and there is a slight movement or no movement at all. Cartilaginous joints are found in the vertebral body, between the manubrium, and in the sternum.
SYNOVIAL TYPES OF JOINTS IN THE BODY
Most permanent joints of the body are synovial. In this type of joint, the ends of bones are covered with cartilage forming a thin, smooth joint. It contains a joint cavity, filled with a clean, thick, viscous oily fluid or synovial fluid, which keeps the joint smooth and nourishes the articular cartilage without blood vessels. The joint is surrounded by a fibrous articular capsule, which contains the lining of the synovial membrane. This lining does not remain on the ends, cartilage, and disc of the joint. The fibrous capsule is attached to a thick layer of collagen fibers called a ligament. Such joints have more independent movements than other types of joints.
The synovial joints can be divided into different classes according to the range of motion occurring in them or the size of the articulating surfaces of the bones.
PIVOT JOINT
In such types of joints, rotation is possible only around the axis or axis. The joint between the cervical atlas vertebra and the odontoid process of the axis vertebra and the radioulnar joint is similar. As the head rotates from one side to the other
GLIDING JOINT
In this type of joint, the articular surfaces of the bones are flat, from which one bone slips on the other bone. Carpal bones and tarsal bones are called gliding joints.
HINGE JOINTS
These are joints that allow moving forward or backward on the same surface, just as occupants with doors move around on one side. The knee joint is the hinge joint. These types of joints are also known as tenon joints. Only flexion and extension can be done in such type of joints. Elbow, knee, ankle, fingers are examples of such joint joints.
CONDYLOID JOINTS
These types of joints are similar to the hinge, but it is possible to have movements in the lateral and anterior two directions. The motion of these joints is around two axles. It is possible to have many types of mobility – flexion, flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, circumduction. But the rotation is not possible. Dynamic joints are protected from many types of damage or wear and tear. The last part of the bones is covered with a flat layer of cartilage. In this way, they move on top of each other. The suppleness under the cartilage breaks the impact of sudden shaking or shock and the quality of the cartilage allows the joints to move freely. A fluid called synovial fluid makes the joints moist and smooth.
GLIDING JOINT
In this type of joint, the articular surfaces of the bones are flat, from which one bone slips on the other bone. Joint joints between vertebral articular tendons, acromioclavicular joints, and joints between the carpal and tarsal bones are similar.
BALL AND SOCKET JOINT
In this type of joint, the round end of one bone fits into the socket of the shape of the cup of the other bone. These joints move in a more oriented manner than all other joints. Shoulder joints and hip joints are similar types of joints.
This joint is the one that provides the most freedom for movement of the limbs. Ball and socket joints are made of marigold on the last edge of the long bone. They are connected in the shell of other bones. The joints of the shoulders and the nimbo are called ball and socket joints. The arms of the body can move more freely, than the legs, because the joints of these organs are formed in this way. The arms can move more because the shoulder girdle is loosely connected to the chest walls.
SADDLE JOINT
In these types of joints, one bone head joins the concave head of the other bone. They have a lot of freedom to rotate their limbs. Such a joint is the joint between the first metacarpal and the trapezium bone of the hand. These joints may have abduction, adduction, opposition, and reposition.
TYPES OF JOINTS IN THE BODY AND ITS MOVEMENT
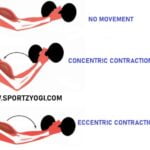
FLEXION:-By this motion, the action of turning the limb to the midline of the body comes. The turning and bending of the limb also come under this motion. Such as bending the elbow or knees.
EXTENSION:-In this motion, it is possible to spread the organ away from the midline of the body. The action of straightening the limb is under this motion. Like- arms stretching.
ABDUCTION:-Moving any part of the body away from the midline of the body is called abduction.
ADDUCTION:-The action of bringing the organ close to the midline of the body is called adduction.
CIRCUMDUCTION: – In this motion, the limb has to be rotated at some distance from the body in a circular motion,
For example, such a motion is made by throwing a cricket ball with the arm.
ROTATION:- Rotation speed on the axis is called rotation speed. Such a motion is caused by the movement of another bone around an amplification of a bone or moving within another bone, such as the movement between the atlas vertebrae and the audontidae amplification of the axis vertebrae.
INVERSION:-There is an act of turning inward. Like- moving the sole inside.
EVERSION:-This motion involves the movement of the limb outward, such as the sole of the foot moving outward.
SUPINATION: – The rotating motion of the forearm in which the radius rotates becomes parallel to the ulna. Or raising the palm or lying straight on the waist.
PRONATION: – The rotating motion of the forearm in which the radius becomes oblique above the ulna or the palm is turned down or backward or lying flat.
OPPOSITION: – It is an angular motion in which the little finger is touched by the thumb. Such motion is only on the carp metacarpal joint of the thumb of the hand.
REPOSITION: – A movement in which the thumb reaches its anatomical position. This is the opposite of opposing the motion.
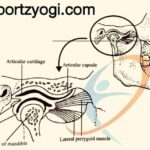
PROTRACTION: – Movement in front such as moving of mandible.
RETRACTION: – Action of pulling backward. Such as pulling the mandible backward.
DEPRESSION: – Downward or inward displacement of a body part
ELEVATION: – Lifting body part upward.
Read more about- After the types of joints in the body you can read more about the chemical composition of the body just click the link below
https://www.sportzyogi.com/chemical-composition-of-the-body/