WHAT IS CARDIAC CYCLE?
CARDIAC CYCLE:- The function of the heart is to maintain a continuous circulation of blood all over the body. This is achieved by the rhythmic contraction of its muscle. The amount of blood in the human body is 4 to 6 liters, but the heart completes a cycle by pumping blood throughout the body in a little more than a minute. On average, an adult person’s heart pumps around 7500 liters of blood throughout the body daily. The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occur in the heart during a single beat. The rate of the heart is 72 beats per minute. Changes that occur in the heart during the duration of one beat also recur in the second beat.
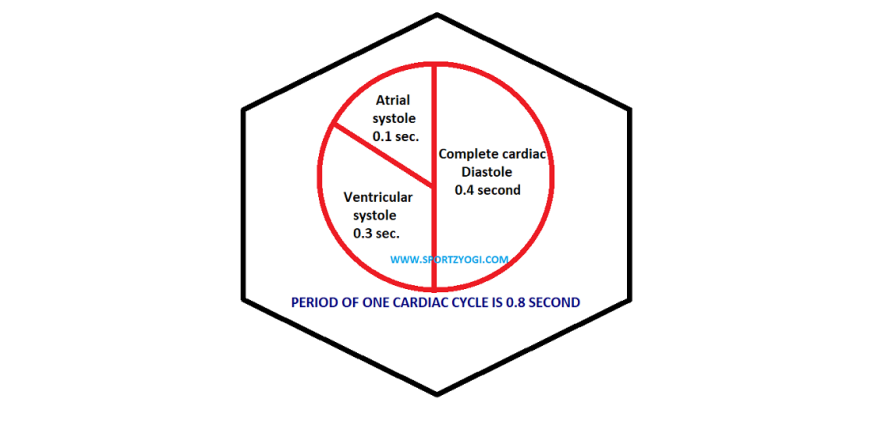
The cyclical repetition of these changes of heart from one beat to another is called a cardiac cycle. Each cycle has a contraction of atrium and ventricles called systole, and relaxation of atrium and ventricles, which is called diastole. In the heart, systolic and diastolic movements occur in a rhythmic order. The duration of a cardiac cycle is 0.8 seconds, that is, every event of each cycle is repeated every 0.8 seconds.
Every cycle occurs in two phases are:-
SYSTOLE- PERIOD OF CONTRACTION
DIASTOLE- PERIOD OF RELAXATION
WHAT ARE THE PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLES?
The cardiac muscle has certain characteristics are as follows:-
Contractility– By contraction of the cardiac muscle, the heart pumps blood out of its Chambers.
Conductivity- The impulses of cardiac contraction are conveyed through a specialized conduction system.
Rhythmicity- Heart muscles have the inherent property of rhythmic contractions. Cardiac contraction occurs in a regular Fashion. The two atria and ventricles contract alternately.
Refractory period- During the period of systole, the heart does not make a response to any other stimuli, however strong it may be. This is called the refractory period.
What are the four phases of the cardiac cycle?
Or four stages of the cardiac cycle
- Atrial systole
- Ventricular systole
- Atrial diastole
- Ventricular diastole

Cardiac cycle
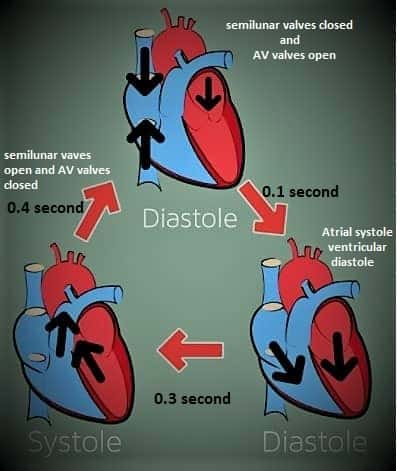
ATRIAL SYSTOLE- During the atrial systole, which has a duration of 0.1 seconds, there is a simultaneous contraction in both atria allowing blood to pass through the tricuspid and mitral valves into both ventricles.
VENTRICULAR SYSTOLE- During ventricular systole, the duration of which is 0.3 seconds, there is a simultaneous contraction in both the ventricles so that the blood goes into the pulmonary artery opening the pulmonary valve located in the right ventricle through which it goes into the lungs to be purified. And in the left ventricle, the aortic valve opens into the aorta, and through its branches and subsections, the blood reaches every part of the body except the lungs.
ATRIAL DIASTOLE- During atrial diastole, which has a duration of 0.7 seconds, the atrial relaxes and the ventricles remain constricted and the atria begin to replenish the heart from the vena cava. The right atria receive blood from the inferior and ventricular veins and the left four pulmonary veins.
VENTRICULAR DIASTOLE –During ventricular diastole, the duration of which is 0.5 seconds, both ventricles are relaxed and the ventricles are filled with blood coming from the atrium. The heart cycle begins with atrial systole. This event ends in 0.1 seconds and the next moment the diastole starts, which lasts for 0.7 seconds. After the atrium-diastole, the atrial-systole is recursive, and the atrial cycle continues, with a total duration of 0.8 seconds.
The ventricular systole begins after the atrial systole, which has a duration of 0.3 seconds. The ventricular diastole begins shortly thereafter, with a duration of 0.5 seconds. At its end, there is a recurrence of ventricular systole and thus the ventricular cycle continues. Its total duration is 0.8 seconds in total.
Ventricular diastole is equivalent to a period of 0.4 seconds in a 0.5 second time period of atrial diastole. Ventricular diastole is a period of 0.4 seconds out of 0.5 seconds. Thus the entire duration of the heart cycle is of 0.4 seconds out of 0.8 seconds in which both the atrial and the two ventricles remain together in a state of diastole, that is, the heart relaxes for 0.4 seconds. This state is also called the normal rest period. The remaining 0.4 seconds works. In this way, the heart spends only half of its life for the rest of its life and spends the remaining half of its time in rest.
CONDUCTING SYSTEM OF THE HEART
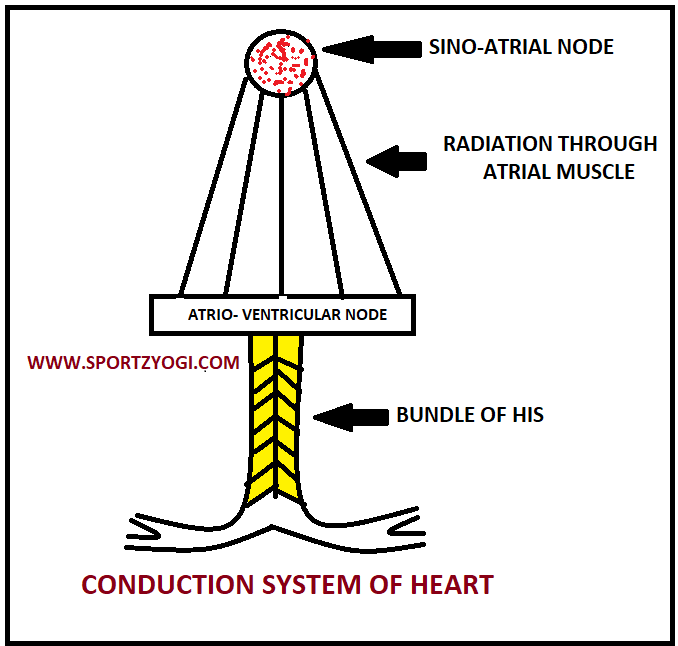
The impulses of cardiac contraction are transmitted through the conduction system of the heart. This system is made of these four:-
Sinoatrial node
Atrio ventricular node
Bundle of HIS
Purkinje fibers

The conduction of impulses occurs in the following sequence:-
- The impulses of cardiac contraction start at the Sinoatrial. It is present at the opening of the superior Vena cava into the right Atrium [SA] node is called a pacemaker of the heart.
- The impulses then pass through the atrial muscle.
- After, the impulses pass to the atrioventricular node. It lies in the upper part of the atrioventricular septum.
- Now from here, the impulses pass to the bundle of “HIS”. It is a unique bundle of nerves and muscular tissue. This is the only connection between the ventricles and atria.
- The bundle of his passes through the interventricular septum. Later it is divided into branches called Purkinje fibers. The right and left branches of this fiber come up with the two ventricles.
- This specialized conduction system of the heart provides greater conductivity for cardiac impulse.
HOW’S THE HEART SOUND?
Total four sounds are produced by the heart but only two sounds can be heard easily. Sounds similar to the pronunciation of the words LUBB- DUP are produced when the heart is functioning. They can be heard by placing the ear directly on the chest near the heart or with a stethoscope.
The FIRST SOUND is caused by the closure of the atrioventricular valves means tricuspid and bicuspid valves. The first sound is produced by the contraction of the ventricles at the beginning of the systole of the ventricles. Hence it is also called systolic sound. This sound is somewhat long, and of long duration [0.12second]. This is the sound of LUBB.
The SECOND SOUND is produced as a result of the closure of the semilunar valves means aortic and pulmonary valves. The second sound occurs during the diastole of the ventricles, so it is called a diastolic sound. It is shrill and of short duration [0.01sec]. This is the sound of DUP.
A THIRD SOUND of the heart is a very low-pitched sound, which is produced during the rapid filling of a cardiac cycle. It occurs in the first part of the diastole; hence it is also called ventricular gallop and protodiastolic. The third sound of the heart cannot be heard with a stethoscope, it can only be heard with the help of a microphone. It is a short and low pitch sound duration of 0.07 sec to 0.10 second
A FOURTH SOUND of the heart is the inaudible sound, which is heard only in the pathological state. It can be studied only by graphical recording or phone cardiology. This sound is produced only during atrial systole. Therefore, it is considered to be a physiologic atrial sound. It is also a short and low pitched sound duration of 0.02 sec to 0.04 sec
WHAT IS CARDIAC OUTPUT?
Cardiac output is described as the quantity of blood pumped by the heart in one minute. Stroke volume is the amount of blood ejected per beat of the heart. It is 70 ml. so every minute some 5 liter of blood pumped by the heart.
Cardiac output depends on the following factors
- Amount of blood returned to the heart through veins
- FORCE and rate of contraction of the heart
- Peripheral resistance offered by blood vessels