VALVES OF THE HEART
What are heart valves and how they work?
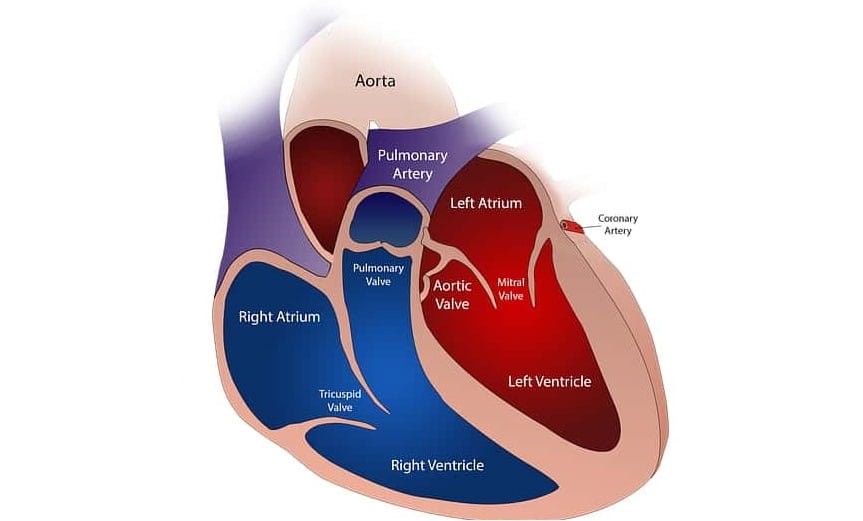
Valves of the heart- Our heart is composed of the four chambers which are the right and left atrium, right and left ventricle, where blood passes through every valve before departing each chamber. Valves manage the flow of blood across the heart. These valves have flaps or cusps that open as blood drain from a chamber. When the flaps close, they obstruct blood from flowing back into the chamber. Valves separate the atria and the ventricle. They are also known as atrioventricular valves or AV valves. Generally, valves have 3 flaps or cusps, but the bicuspid or mitral valve has only two flaps.
The four heart valves are:-
TRICUSPID VALVE
The position of the right atrioventricular orifice between the right atrium and the right ventricle is called the tricuspid valve. It consists of three triangular cusps [three flaps], each strengthened by fibrous tissue with a double folded Endocardium. From the lower surface of the cusps, there are many thin tendon lines which are called tendon cords or chordae tendinae. It originates from the papillary muscles of the ventricle. It is because of these ropes that the cusps of the valves always remain in place. These cusps of the valves have complete control over the atrioventricular orifice. A contraction of the atrium pushes the blood to the cusps and enters the ventricle. Shortly thereafter, the cusps close and at the same time, the papillary muscles become compressed and stretch on the chordae tendinae, preventing the cusps from being pushed into the atrium and the blood is not able to return.


PULMONARY VALVE
The valve is situated within the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery is called the pulmonary valve. It has three semilunar cusps hence it is also called a semilunar valve. The cusps are attached to the wall of the artery by its folded edges, while the straight edge remains free and thus three pockets are formed in front of the artery. As the blood flows from the left ventricle to the pulmonary artery i.e. in the right direction, these pockets flatten away from the vessel wall, but when the ventricle is relaxed and the blood tries to flow in the wrong direction ie from the artery to the ventricle. These pockets are filled with blood and spread together and close the hole completely in the middle.
BICUSPID VALVE / MITRAL VALVE
The valve of the atrioventricular orifice between the left atrium and the left ventricle is called the mitral valve or bicuspid valve. It consists of two cusps. The composition is like a tricuspid valve. It does not allow blood to return to the left atrium during the contraction of the left ventricle.


AORTIC VALVE
This valve is situated between the left ventricle and the aorta. The left ventricle squeezes blood into the aorta. Its composition and function are similar to pulmonary valves.
What are the diseases of valves?
Valvular stenosis [valves becomes narrow]
It occurs in the heart when the opening of the valve becomes shrink or stiffen and does not fully open. Due to the narrowing of the valves, there is a lot of difficulty in pumping blood to the heart, which causes heart failure. It can occur in all four valves which we call tricuspid stenosis, mitral stenosis, pulmonic stenosis, and aortic stenosis.
Regurgitation of valves [leakage of valves]
In this case, the valves are not completely closed so that the blood does not fully pass into the other chamber and the blood moves back from the ventricle to the atria, also known as blood leakage. In other words, valves open and close in every cardiac cycle, but due to some reasons, they become dysfunctional and leakage occurs.
SYMPTOMS OF HEART VALVE DISEASE
- Chest pain,
- Fatigue,
- Loss of consciousness,
- Shortness of breath,
- No rapid or irregular heartbeat,
- Chest heaviness,
- Dizziness,
- Faint sometimes.
When there is any problem such as shrinkage or leakage, then it gets over the heart and the heart starts working faster to complete this deficiency but after a time the heart starts to fail and the symptoms of heart failure Seem to happen. Dysfunction in the valves of the heart can be detected by echocardiography, which we also call 2D Doppler; it is usually ultrasound of the heart.
CAUSES OF HEART DISEASE
Rheumatic heart disease
It is a type of bacterial infection that occurs due to a lack of proper treatment of recurrent throat infections in childhood. Later on, these bacteria affect the heart valves and further cause problems in the valves. This disease is more commonly seen.
Degenerative causes
It is found in older people, aged patients who are 50 to 70 years or more, their valves start to be DEFORM. Because with increasing age, the valves become thicker or calcium accumulates in them and they start to shrink or leakage.
Congenital and genetics
Excessive loosening of valves so that they do not function properly may be genetic.