Sociological Basis of Physical Education
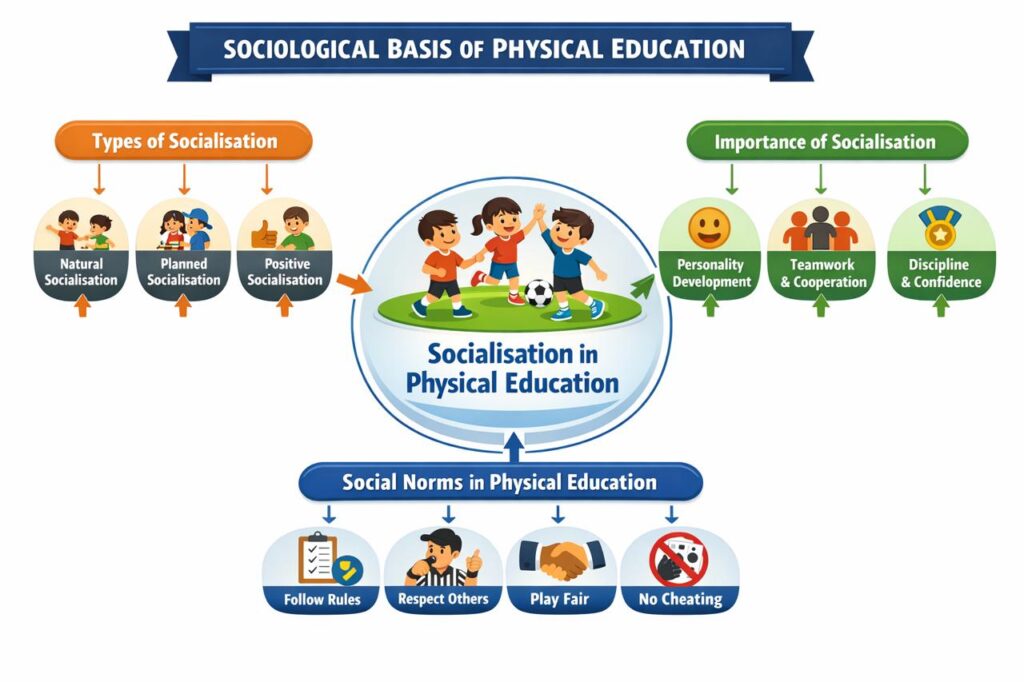
The sociological basis of physical education explains the relationship between physical education and society. One of the most important concepts in this area is the socialisation process. Socialisation helps individuals learn social behaviour, values, and cultural norms through interaction with others.
Physical Education plays a key role in socialisation because sports and physical activities provide real-life situations where students learn cooperation, discipline, leadership, and respect.
Socialisation Process in Physical Education
Socialisation is the process through which individuals learn the culture, values, behaviour, and social rules of society. A child is not born with social knowledge. This learning happens through parents, teachers, peers, schools, and social institutions.
In Physical Education, socialisation occurs naturally during games and sports. When students participate in team games, they learn how to follow rules, respect teammates, accept decisions, and work together for common goals. Physical activities help students understand their role as team members, leaders, or followers.
Socialisation also helps students learn social norms, which are the accepted rules and expected behaviour of society. In Physical Education, norms include fair play, discipline, honesty, and respect for opponents and officials.
The term enculturation refers to learning and adopting the culture of a particular society. Traditional and indigenous games such as kabaddi, kho-kho, and wrestling help students connect with cultural values while improving physical fitness.

Importance of Socialisation Process in Physical Education
1. Socialisation helps in overall personality development. Physical Education builds confidence, discipline, and emotional balance.
2. Personality is shaped not only by genetics but also by environment and experiences. Sports provide positive social experiences.
3 . Socialisation explains differences in behaviour among individuals from different societies. Team sports promote cooperation and unity.
4 . Learning through Physical Education is enjoyable and meaningful. Rules, rewards, and penalties teach responsibility and self-control.
5. Early exposure to sports helps children develop social skills that remain useful throughout life.
6. Socialisation is a lifelong process. Learning continues from childhood to adulthood through physical activities.
Classification of Socialisation in Physical Education
1. Natural Socialisation
Natural socialisation occurs when children learn social behaviour through free play and informal activities. In Physical Education, recreational games and unstructured play help children interact freely and learn social values naturally.
⸻
2. Planned Socialisation
Planned socialisation takes place through organised teaching and training. In Physical Education, teachers and coaches plan activities, drills, and competitions to develop discipline, teamwork, and leadership skills. School sports programs are examples of planned socialisation.
⸻
3. Positive Socialisation
Positive socialisation is based on encouragement, appreciation, and enjoyable learning experiences. In Physical Education, motivation, rewards, and supportive coaching help students develop a positive attitude towards sports and physical activity.
⸻
4. Negative Socialisation
Negative socialisation occurs when learning is based on punishment, fear, or harsh criticism. In Physical Education, excessive punishment may reduce confidence and interest. Therefore, positive methods are more effective for long-term development.
⸻
Role of Physical Education in Social Development
Physical Education helps students become responsible members of society. Through sports, students learn cooperation, leadership, discipline, and respect for rules. Thus, Physical Education plays a vital role in building a healthy and socially balanced society.
⸻
FAQs
Q1. What is the sociological basis of physical education?
It explains how Physical Education helps in social development, cultural learning, and social behaviour.
Q2. How does Physical Education help in socialisation?
Through sports and games, students learn teamwork, discipline, leadership, and respect.
Q3. What are the types of socialisation in Physical Education?
Natural, planned, positive, and negative socialisation.